Brute force attack is arguably one of the most common and potentially dangerous threats to WordPress websites.
A brute force attack involves hackers trying to guess your WordPress login credentials by repeatedly submitting different combinations of usernames and passwords. If they succeed, they can take over your entire website and cause serious damage.
In this article, we will discuss various types of brute force attacks, and show you how to protect your WordPress site by using some simple but effective methods.
Let’s get started!
What is a Brute Force Attack?
Brute force attacks are a serious cybersecurity menace. In this type of attack, threat actors continuously attempt every conceivable password or encryption key combination until they find the correct one. These attacks can be quite resource-intensive and time-consuming for attackers, particularly when robust passwords are in place.
However, because of its sheer simplicity, even an unskilled attacker can perform this attack.
Let’s discuss what would happen if an attacker can guess your password:
- Lose Access to Your Website and Data: If a brute force attack is successful, the attacker gains unauthorized access to your website. This can lead to a loss of control over your site, making it difficult to manage, and potentially even resulting in data loss.
- Website Defacement and Malware: Once an attacker gains access, they may deface your website by altering its content, and layout, or injecting malicious code. This not only damages your website's reputation but also poses a risk to your visitors, who may be exposed to malware.
- Spamming and Phishing: Hackers often use compromised websites to send out spam emails or launch phishing campaigns. This not only tarnishes your brand's reputation but can also lead to legal consequences if your website is used for fraudulent activities.
- Search Engine and Hosting Provider Blacklisting: Brute force attacks can lead to your website's IP address or domain being blacklisted by search engines or hosting providers. This means your site may not appear in search results, and your hosting account could be suspended or terminated, disrupting your online presence.
- Reputation and Trust Erosion: A compromised website can severely damage your reputation and trust among visitors and customers. People may lose faith in your site's security and credibility, impacting your business and brand image.
- Financial Consequences: Recovering from a successful brute force attack can be costly. You may need to invest in security enhancements, engage in damage control, and potentially compensate affected users or clients – depending on the nature of the breach.
- Legal and Compliance Issues: If personal or sensitive data is exposed due to a successful attack, you may face legal and compliance issues, including fines for not adequately protecting user information. This is especially true if your website handles customer data, such as payment information.
- Downtime and Lost Revenue: If your website is compromised or suspended due to a successful attack, you'll experience downtime, resulting in lost revenue and opportunities. Customers may turn to competitors in the absence of your services.
Types of Brute Force Attack
There are many different types of brute force attacks. Let’s break down some of the most common ones:
- Simple Brute Force Attacks: These involve manually guessing login credentials without using any software. Attackers try standard password combinations or common PIN codes. Weak passwords like “password123”, or using the same password across multiple sites are vulnerable to this method.
- Dictionary Attacks: In this basic form, attackers test possible passwords against a specific username. They run through dictionaries, modifying words with special characters and numbers. While time-consuming, it’s still used by some hackers because of its effectiveness against weak passwords.
- Hybrid Brute Force Attacks: Combining dictionary and simple brute force methods, attackers start with a known username. They experiment with character, letter, and number combinations to find the correct password (e.g., “SanDiego123”).
- Reverse Brute Force Attacks: Here, attackers begin with a known password (usually from a network breach). They then search for matching login credentials among millions of usernames.
- Rainbow Table Attacks: While not strictly brute force, it is a cunning method to break passwords. These attacks leverage precomputed tables filled with hashed values for commonly used passwords. Attackers use these tables to look up original passwords corresponding to their hashed counterparts.
The effectiveness of rainbow table attacks is largely contingent on whether the website has implemented password salting. Salting involves the addition of a random value to a password before hashing it, rendering precomputed tables, such as rainbow tables, largely ineffective. This simple yet critical security measure greatly increases security and is resistant to rainbow table attacks.
How to Prevent Brute Force Attack on WordPress
Fortunately, there are several ways to protect your WordPress website against brute force attacks. In this section, we will show you some of the best practices and tools that you can use to secure your WordPress login and prevent unauthorized access.
Using a Password Manager
Password managers play a pivotal role in defending against brute force attack. They can be used to create lengthy, intricate, and virtually uncrackable passwords, protecting websites against automated intrusion attempts.
The primary strength of password managers lies in their ability to generate and securely store unique, robust passwords for each site, effectively eradicating the risk of credential stuffing and dramatically enhancing overall security.
Additionally, password managers make it easy to use different passwords everywhere, discouraging the practice of recycling passwords across multiple sites. By avoiding reusing passwords you can make it difficult for attackers to compromise multiple accounts with a single stolen password.
Limiting Login Attempts
Limiting login attempts is an immensely effective security practice to protect your WordPress site against brute-force attacks. By restricting the number of login retries allowed per IP address, you can greatly reduce the chances of a successful brute-force attack.
If you are implementing this on your site, you should know that many solutions also have the option to modify the amount of time a user or IP must wait after a lockout, and also configure the remaining number of retries. This prevents repeated login attempts within short intervals.
Using Two-Factor Authentication
Two-factor authentication (2FA) adds an extra layer of security to your WordPress login by requiring a code from your phone or another device in addition to your password. This way, even if someone guesses or steals your password, they cannot access your website without the code.
There are different ways to implement two-factor authentication on WordPress, including:
- Use an app such as Google Authenticator or Authy that generates codes on your phone.
- Use an email service such as GuardGiant that sends codes to your email address.
- Use a hardware device such as YubiKey or Titan Security Key that plugs into your computer.
To use 2FA on your WordPress website, you’ll need to install a plugin that supports the method you choose.
For example, if you want to use Google Authenticator, you’ll need to install the Google Authenticator plugin on your WordPress dashboard, and then follow the instructions to set up the plugin (including scanning the QR code with your phone).
Using a Captcha
A captcha is an automated challenge that requires human input, such as typing a word or clicking on an image. By using it, you can filter out automated brute-force attempts and reduce the load on your server.
There are different types of captchas available for WordPress. To use a captcha on your WordPress website, you’ll need to install a plugin that supports the type you choose.
For example, if you want to use Google ReCaptcha, you’ll need to install the Google Captcha plugin on your WordPress dashboard. Then follow the instructions to register for a Google ReCaptcha account and configure the plugin settings.
Using Patchstack
Patchstack provides several robust login protection features. Let’s delve into why Patchstack is an exceptional solution for mitigating brute-force attacks on your WordPress websites:
- Block wp-login.php Access: By restricting access to the default login page, you prevent attackers from hammering it with brute force attempts.
- Automatic IP Ban: Failed login attempts trigger automatic IP bans, thwarting repeated attacks.
- Login Hours Enforcement: With Patchstack, you can specify allowed login times to further secure your site.
- Whitelisting and Blacklisting: You can whitelist specific IP addresses (e.g., yours) to ensure uninterrupted access. Conversely, Patchstack automatically blocks IPs with excessive failed login attempts.
- Add reCAPTCHA: Patchstack supports Google’s invisible (v3) reCAPTCHA and uses it to block automated attacks on WordPress core interactions such as posting comments, user login, registration, and password reset forms.
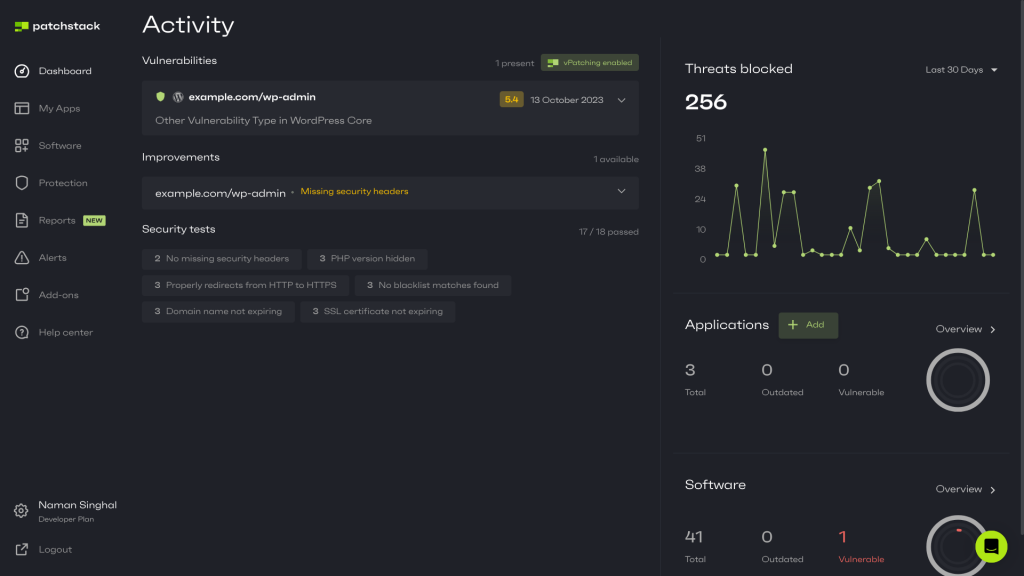
Furthermore, Patchstack provides real-time vulnerability detection. It continuously monitors your plugins, themes, and WordPress core for new security issues. You’ll receive alerts about vulnerabilities 48 hours before they become public – even on the FREE plan! When a vulnerability is detected, Patchstack offers vPatches. These are targeted fixes that protect your site without waiting for official security updates.
Conclusion
Brute force attack is a serious threat to WordPress websites, but they can be prevented with some simple steps and tools. By following the best practices and using the tools mentioned in this article, you can protect your WordPress website against brute force attacks, keeping it safe and secure.
Patchstack combines proactive vulnerability detection, vPatches, and intelligent login protection to keep your WordPress sites secure. Even on the free plan, you get real-time vulnerability detection and 48h early warning. Don’t wait until it’s too late - sign up to Patchstack today and fortify your website’s security! 🔒🔐