This blog post is about the Flatsome theme vulnerability. If you're a Flatsome user, please update the plugin to at least version 3.17.6.
✌️ Our users are protected from this vulnerability. Are yours?
Identify vulnerabilities in your plugins and get recommendations for fixes.
Request auditProtect your users, improve server health and earn additional revenue.
Patchstack for hostsAbout the Flatsome Theme
The theme Flatsome (versions 3.17.5 and below, premium version), which is estimated to have over 660,000 active installations, is one of the best-selling WooCommerce themes at ThemeForest. This plugin is developed by UX-Themes.

This theme is a premium builder focused for the WooCommerce site development. Flatsome is the theme claimed to be suitable for an agency or freelancer. It has got all the tools needed to create super-fast responsive websites with amazing user experience. It has got unlimited options and a revolutionary responsive page builder, so we can create anything without coding.
The security vulnerability
The Flatsome theme suffers from an unauthenticated PHP Object Injection vulnerability. This issue occurs when user-supplied input is not properly sanitized before being passed to the maybe_unserialize function which is a wrapper for PHP unserialize function.
Since PHP allows object serialization, an unauthenticated user could pass ad-hoc serialized strings to a vulnerable unserialize call, resulting in an arbitrary PHP object(s) injection into the application scope. The described vulnerability was fixed in version 3.17.6 and assigned CVE-2023-40555.
The underlying vulnerability exists in the flatsome_ajax_load_instagram function:
function flatsome_ajax_load_instagram () {
$data = isset( $_GET['data'] ) ? (string) $_GET['data'] : '';
list( $hash, $value ) = explode( ':', $data, 2 );
if ( empty( $value ) || empty( $hash ) ) {
wp_send_json_error( 'Invalid data' );
}
$atts = maybe_unserialize( base64_decode( $value ) );
$tick = ceil( time() / MONTH_IN_SECONDS );
$expected = substr( wp_hash( $tick . $value ), -12, 10 );
if ( ! hash_equals( $expected, $hash ) ) {
wp_send_json_error( 'Invalid hash' );
}
$atts['loading'] = 'eager';
$markup = ux_instagram_feed( $atts );
wp_send_json_success( trim( $markup ) );
}
add_action( 'wp_ajax_flatsome_load_instagram', 'flatsome_ajax_load_instagram' );
add_action( 'wp_ajax_nopriv_flatsome_load_instagram', 'flatsome_ajax_load_instagram' );We could see that the flatsome_ajax_load_instagram function is set as a function handler for the wp_ajax_nopriv_flatsome_load_instagram ajax action which indicates that the function can be reached by an unauthenticated user. The function will directly process the base64-decoded $value to the maybe_unserialize function. The $value itself is constructed from $data which directly comes from $_GET['data'] without any filtering or sanitization. Since the user can fully control $value, we can achieve arbitrary PHP object injection on the server.
Note that this vulnerability can be triggered on a default installation or configuration of the Flatsome theme without any additional setup requirements.
At the time this article was published, we were not able to discover a significant POP chain in the vulnerable plugin, making the impact of this issue limited. If a POP chain is present via an additional plugin or theme installed on the WordPress site, it could allow the attacker to delete arbitrary files, retrieve sensitive data, or execute code, depending on the available POP chain.
The patch
Since the issue is mainly because the plugin uses the unsafe maybe_unserialize function, replacing the function should be enough to fix the issue. In this case, the vendor decided to use the JSON format to process the $value data. The patch can be seen below:
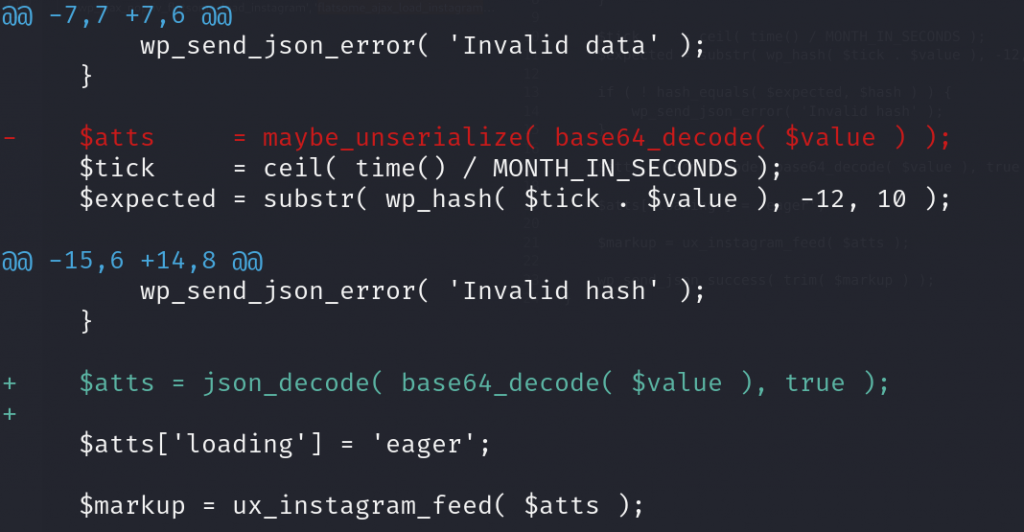
Conclusion
The maybe_unserialize function is a wrapper for PHP unserialize function which is one of the more sensitive processes that could lead to a security issue. In general, we do not recommend using this method to process data that could be partially or fully controlled by user input.
We recommend using JSON instead of serialization to process more complex data structures. If the unserialize process is still needed on the application, we recommend at least configuring the allowed_classes option set to false.
Timeline
🤝 You can help us make the Internet a safer place
Streamline your disclosure process to fix vulnerabilities faster and comply with CRA.
Get started for freeProtect your users too! Improve server health and earn added revenue with proactive security.
Patchstack for hostsReport vulnerabilities to our gamified bug bounty program to earn monthly cash rewards.
Learn more