Google has a significant impact on web traffic for many businesses, and if it detects spam pages or manipulative SEO techniques on your website, the consequences can be severe.
While some website owners intentionally use manipulative techniques like SEO spam and cloaking to game the system, it's possible to employ these tactics accidentally without realizing it.
This article will explore SEO spam and cloaking, how they can harm your website, and, most importantly, how to ensure your SEO practices remain ethical and effective.
Let’s begin!
What is SEO spam?
Most people will discover your website through a search engine when they search for relevant information. However, some people try to trick search engines to manipulate search results and gain more traffic. This is usually done by stuffing unnecessary keywords or search terms in the website without providing any actual useful information to the users.
Alternatively, when an attacker has compromised a website, the attacker can create sub-pages and hide links and keywords in the source code of your site. This allows attackers to direct traffic to their website by using your site, which is also considered spam because users are being shown content they didn’t opt for.
There are several ways for attackers to inject spam into your site, such as software vulnerabilities, outdated plugins, or theme vulnerabilities, and obviously, when your admin user password is “admin” or something equally poor and easy to guess.
Interestingly, a site doesn't always need to be hacked for spammers to take advantage.
Some websites, especially those with internal search functions or dynamic content, automatically generate new URLs based on user queries or parameters. Spammers can exploit this feature by creating a massive number of URLs with different query strings.
For example, an e-commerce site might create a new URL for every product search, like "example.com/search?q=buy my trading course from www.mywebsite.com". Spammers can flood search engines with variations of these URLs, even if the content doesn't exist on your site.

How to check if your site has SEO spam
You can use a simple yet effective Google search technique to check whether your website has fallen victim to SEO spam.
Open your preferred web browser and head to Google's search page. In the search bar, type in the following command: site:mywebsite.com intext:canadian pharma (replace "mywebsite.com" with your domain name).
Replace the ‘intext’ search term with the following examples for a broader sweep (yes, they look silly, but this is a quick and effective method):
- intext:viagra
- intext:cialis
- intext:designer clothes
- intext:canadian pharma
- intext:sexual function
- intext:erectile dysfunction
This specialized search tells Google to look for pages on your website containing the phrase "canadian pharma" – a common term used in pharmaceutical spam. Once you hit “Enter”, carefully examine the search results. If you see pages or content you don't recognize or didn't create yourself, it's a red flag that SEO spammers may have compromised your site.
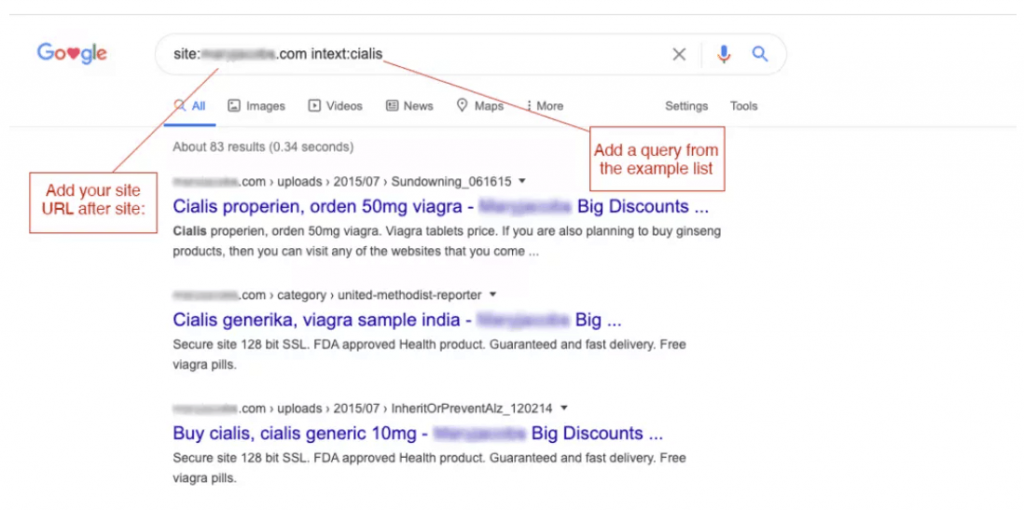
These unexpected results could include new pages about medications, online pharmacies, or other health-related topics that are uncharacteristic of your website's usual content. If you spot such anomalies, it's time to immediately clean up your site.
In addition to the Google search technique mentioned earlier, you can use the Google Search Console to monitor your website's health and detect potential SEO spam. You should regularly check your Google Search Console account for unusual activity and pay close attention to the "Coverage" and "URL Inspection" reports.
These reports can reveal pages that Google is crawling, but you don't recognize. Look for sudden spikes in indexed pages, especially if the number is much higher than expected. If you notice unfamiliar URLs in these reports, it could indicate that spammers have injected content into your site.
What is cloaking?
Cloaking is a search engine optimization technique in which the content presented to the search engine spider is manipulated to rank higher in search results. The content presented to the user’s browser differs from the content presented to the search engine.
Cloaking is considered a violation of Google search policies because it provides users different results from those expected. Businesses use SEO to generate site traffic to increase revenue and sign-ups. If they rely on these unethical practices to improve their search rankings, users will lose trust in Google’s ability to produce good search results. Therefore, if Google suspects that a site is hiding its real content, then it penalizes its search rankings.
It is important to note that as you try to use SEO to bring traffic to your site, ill-intentioned hackers do the same.
If a site gets hacked, it is not uncommon for the hacker to use cloaking to keep the hack hidden and harder to find. But why would such hackers be interested in using your site? Since they focus on selling illegal products or services, their sites would be taken down rapidly, and no site means no business. Using your website reduces the risk to them – and there are plenty of websites vulnerable to their hacking attempts to allow them to enjoy a wide presence on the web.
There are a staggering number of outdated and poorly protected websites, all of which can be easily harvested by ill-intentioned hackers. As seen in the screenshot below, these hackers are using websites to redirect traffic to very shady places:
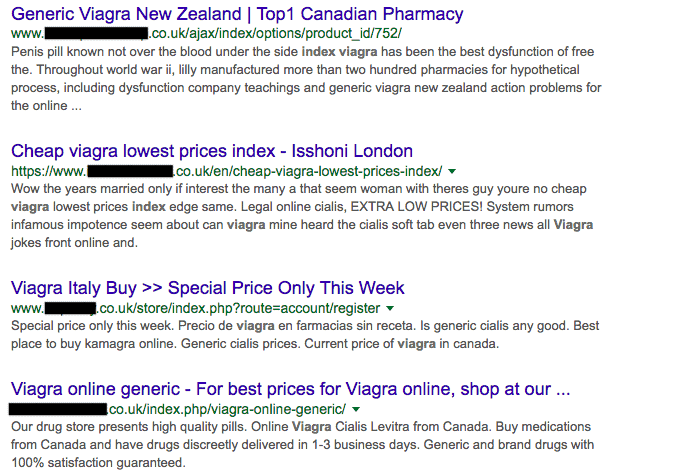
Sites redirecting traffic to an illegal drug store.
These websites listed in the screenshot above are not actually in the business of selling Viagra or any of the drugs mentioned. One of these sites is supposed to sell brand shoes, and another provides business consulting services.
As a web security company, we have seen thousands of cloaking incidents over the years – including kindergarten sites selling Viagra, school sites selling fake designer bags, and some that unknowingly sell essay writing services.
Since cloaking is meant to be invisible to most people, it often stays undetected on the site for a long time until either someone notices it or Google adds the site to its blacklist.

Different methods of cloaking
There are different methods of cloaking. We have listed some of them below.
Referrer cloaking
Referrer cloaking uses the HTTP referer header to show different content based on the visitor's origin. This technique can display specific content to search engine bots while showing something else to regular users, potentially manipulating search rankings.
IP cloaking
IP cloaking serves different content to visitors based on their IP address and often distinguishes between search engine bots and regular users. This method can show optimized content to search engines while presenting different information to human visitors, which violates search engine guidelines.
User-agent cloaking
User-agent cloaking relies on the user-agent string sent by browsers to identify the type of device or software accessing the website. This technique can serve tailored content to different visitors by detecting specific user agents, potentially hiding certain information from search engines.
JS cloaking
JavaScript cloaking displays different content to users with JavaScript enabled versus those disabled or unsupported. Since most search engine bots don't execute JavaScript, this method can be used to show them content that is different from what human visitors with JavaScript-enabled browsers see.
HTTP Accept-Language header cloaking
This cloaking method uses the Accept-Language HTTP header to serve different content based on the user's preferred language settings. While it can be used legitimately for localization, it can also be misused to show search engines content in one language while presenting users with content in another without their consent.
How to avoid cloaking
If you’re using any advanced web development framework, you can probably serve different pages to different users. This is a very useful feature as it allows you to serve location-specific information to users around the world, but it can also be problematic if Google mistakes it for cloaking.
Here’s how to avoid accidentally cloaking your site:
Make sure your mobile and desktop sites show the same primary content
Always keep the core information on your website consistent across all devices. This means the text, images, and videos important to your message should appear on your desktop and mobile versions.
While you might adjust the layout or design for better mobile viewing, the essential content should remain the same to avoid suspicion of cloaking.
Don't hide important text or links from mobile users
Resist the temptation to hide content on mobile devices, even if you're trying to save space. If information or navigation links are important enough to show on a desktop, they should be accessible on mobile, too.
Instead of hiding this content, consider creative ways to present the information, such as expandable sections or a well-designed mobile menu, ensuring all users have equal access to your site's content.
If you use different languages, use proper tags to index these pages on search engines
Use the appropriate HTML language attributes and ‘hreflang’ tags when your website offers content in multiple languages. These tags tell search engines which language each page is in and whether alternative language versions are available.
This proper labeling ensures search engines understand your site structure and can serve users the correct language version, preventing any misinterpretation as cloaking.

To sum it up
SEO spam and cloaking are serious threats that can destroy your website's search engine rankings. When hackers exploit your site for their gain, your hard-earned SEO efforts can all be in vain, leading to a sharp decline in your visibility on search engine results pages.
To safeguard your WordPress website, you must use a robust security solution such as Patchstack, built by a team of reputed white hat hackers working within the WordPress community.
Patchstack offers comprehensive protection against various threats, such as automated logins and brute force protection.
Don't wait until it's too late – sign up for Patchstack today and take proactive steps to protect your website!