Everest Forms
PHP Object Injection
IMPORTANT UPDATE: On 3rd September, we got information on our Discord channel that this vulnerability is not practically exploitable due to the plugin initially checks if the current PHP version used on the server is below 7.1.3, and the plugin will not operate if the PHP version used is below 7.1.3, making the vulnerable code can't be reached. However, we still recommend updating the plugin to at least version 3.2.3 since a security enhancement was made to the reported function. Vulnerability and CVE entry have been revoked for this issue.
This blog post is about an unauthenticated PHP object injection vulnerability in the Everest Forms plugin. If you're an Everest Forms user, please update the plugin to at least version 3.2.3.
✌️ Our users are protected from this vulnerability. Are yours?
Identify vulnerabilities in your plugins and get recommendations for fixes.
Request auditProtect your users, improve server health and earn additional revenue.
Patchstack for hostsAbout the Everest Forms plugin
The plugin Everest Forms, which has over 100,000 installations, is a forms plugin offering contact forms, payment forms, surveys, and similar. It allows for the creation of a variety of different forms using its built-in WYSIWYG style editor. The plugin is developed by WPEverest.
The security vulnerability
In version 3.2.2 and below, Everest Forms is vulnerable to PHP object injection in certain WordPress environments when an Administrator user views form submissions. The plugin allows forms to be submitted with serialized data in many fields. When an admin reviews these submissions, if serialized data is detected, the plugin then attempts to unserialize it before displaying the contents.
A PHP object injection vulnerability can be exploited by passing a serialized string that initializes an instance of a different PHP class, also potentially passing data to this class initialization. This type of vulnerability can be used to exploit flaws in other classes, even ones not directly used by the plugin, leading to a range of potential impacts. You can learn more about PHP object injection in our Academy article.
In the vulnerable versions of Everest Forms, the plugin provides a custom wrapper, evf_maybe_unserialize, for PHP's unserialize function. While this wrapper correctly applies the allowed_classes filter to prevent initializing new objects on modern PHP versions, the wrapper does not use these filters on older (< 7.1) PHP versions, allowing an object injection attack to still be triggered.
function evf_maybe_unserialize( $data, $options = array() ) {
if ( is_serialized( $data ) ) {
if ( version_compare( PHP_VERSION, '7.1.0', '>=' ) ) {
$options = wp_parse_args( $options, array( 'allowed_classes' => false ) );
return @unserialize( trim( $data ), $options ); //phpcs:ignore.
}
return @unserialize( trim( $data ) ); //phpcs:ignore.
}
return $data;
}In this vulnerability, the unserialization process is triggered through the column_form_field function, used in displaying entries in the Admin Dashboard:
public function column_form_field( $entry, $column_name ) {
$field_id = str_replace( 'evf_field_', '', $column_name );
$meta_key = isset( $this->form_data['form_fields'][ $field_id ]['meta-key'] ) ? strtolower( $this->form_data['form_fields'][ $field_id ]['meta-key'] ) : $field_id;
if ( ! empty( $entry->meta[ $meta_key ] ) || ( isset( $entry->meta[ $meta_key ] ) && is_numeric( $entry->meta[ $meta_key ] ) ) ) {
$value = $entry->meta[ $meta_key ];
if ( evf_is_json( $value ) ) {
$field_value = json_decode( $value, true );
$value = $field_value['value'];
}
if ( is_serialized( $value ) ) {
$field_html = array();
$field_value = evf_maybe_unserialize( $value );
// TRIMMED HEREThe vulnerability has been patched in version 3.2.3 and is tracked with CVE-2025-52709.
The patch
In version 3.2.3, the vendor patched this vulnerability by disabling unserialization in the evf_maybe_unserialize function for PHP versions older than 7.1.
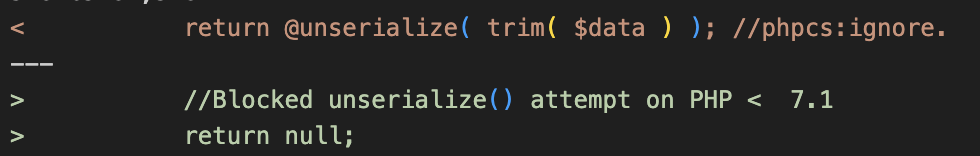
This small change ensures that on legacy PHP releases, unserialization is skipped entirely, completely blocking this vulnerability from executing. For modern PHP releases, the plugin still uses unserialize with the allowed_classes option set to "false", which is a safe way of performing PHP unserialization if a serialization format with less potential risk, such as JSON, cannot be used instead.
Conclusion
There are many ways to store complex data, and within PHP ecosystems, serialize/unserialize have historically been a popular choice. However, PHP's ability to initialize objects during the unserialization process comes with significant security risks, especially when user-provided data is involved. When building new software, the safer choice is to opt for data formats with minimal side effects, such as JSON. These formats limit deserialization to simple types, like arrays, strings, and numbers; this avoids the complex object-related behavior that makes vulnerabilities like this one possible.
When building on existing software that needs to support already existing data, completely changing data storage formats is not always possible. In these cases, unserialize can still be used safely, but it must be used with the allow_classes option to limit object initialization to only specific classes, or none at all.
Want to learn more about finding and fixing vulnerabilities?
Explore our Academy to master the art of finding and patching vulnerabilities within the WordPress ecosystem. Dive deep into detailed guides on various vulnerability types, from discovery tactics for researchers to robust fixes for developers. Join us and contribute to our growing knowledge base!
Timeline
🤝 You can help us make the Internet a safer place
Streamline your disclosure process to fix vulnerabilities faster and comply with CRA.
Get started for freeProtect your users too! Improve server health and earn added revenue with proactive security.
Patchstack for hostsReport vulnerabilities to our gamified bug bounty program to earn monthly cash rewards.
Learn more